ZW20-12Foutdoor Pole mounted high-voltage vacuum Circuit Breaker is an Outdoor High-voltage Switchgear with a rated voltage of 12kVand three-phase AC 50Hz. Mainly used for breaking and closing load current, overload current, and sho-circuit current in power systems. Suitable for protection and control in substations, industrial and mining enterprises, and urban and rural distribution networks, especially suitable for places with frequent operations and urban networkautomation distribution networks. is product is compatible with the controller and can meet the requirements of the distribution automation system, while also reliably and eectively completing the traditional recloser function. It adopts a mature box type sealing structure and is lled with SF6 gas inside, which has good sealing peormance and is not aected by the external environment. It is a maintenance free product. Its spring operated mechanism adopts a direct acting chain main transmission and a multi-stage trip system, with high reliabilityof action, making it a good product for column mounted circuit breakers.
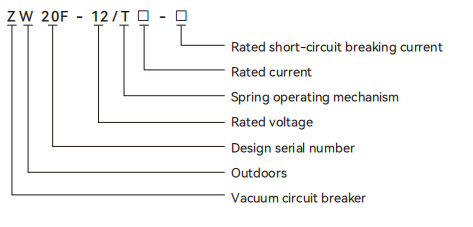
1.Model and meaning
2.Main technical parameters
| Number | Project | Unit | Parameter |
| 1 | Rated voltage | kV | 12 |
| 2 | Rated frequency | Hz | 50 |
| 3 | Rated current | A | 630 |
| 4 | Rated sho比-circuit breaking current | kA | 20 |
| 5 | Rated peak making current | kA | 50 |
| 6 | Rated dynamicstable current peak value | kA | 50 |
| 7 | 4s thermal stable current | kA | 20 |
| 8 | Rated operating sequence |
| Minute -0.3s- combined minute
-180s- combined minute |
| 9 | Rated energy storage motor voltage | V | AC220 |
| 10 | Maximum/minimum energy storage motor voltage | V | AC242/187 |
| 11 | Rated closing operating voltage | V | AC220 |
| 12 | Maximum/minimum closing operation voltage | V | AC264/143 |
| 13 | Rated opening operating voltage | V | AC220 |
| 14 | Maximum/minimum opening operating voltage | V | AC264/143 |
| 15 | Closing at diferent stages | ms | ≤2 |
| 16 | Opening at diferent stages | ms | ≤2 |
| 17 | Rated pressure of SF6 gas (gauge pressure) | Mpa | 0.01 |
| 18 | Rated short-circuit current breaking frequency | Once | 30 |
| 19 | Mechanical lifespan | Once | 10000 |
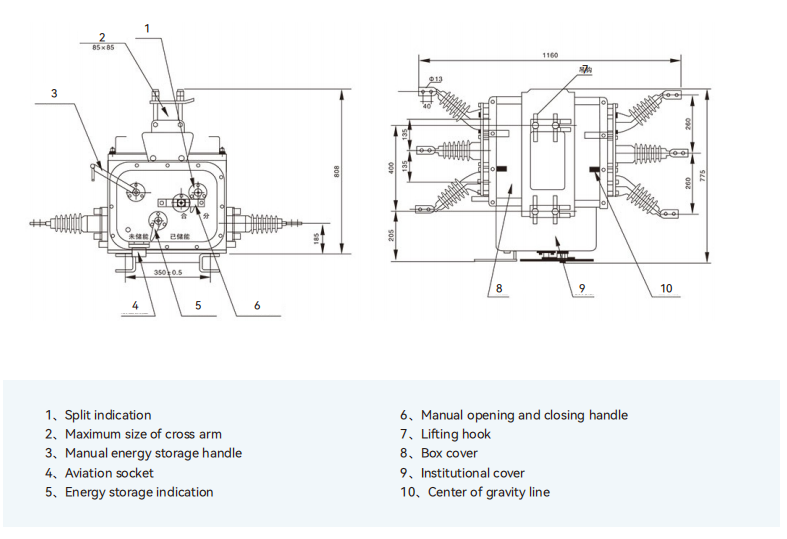
2.Outline and installation dimension diagram
Working principle of circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an essential electrical safety device used to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. It automatically interrupts the flow of electricity when a fault is detected, preventing damage to appliances, wiring, and electrical components.
Basic Function
The primary function of a circuit breaker is to interrupt the flow of electricity in the event of an overload or short circuit. The circuit breaker senses these abnormal conditions and opens the electrical circuit to stop the current, thus preventing further damage. Once the fault is cleared, the circuit breaker can be manually or automatically reset to restore the flow of electricity.
Types of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers come in different types, including:
Thermal Circuit Breakers: These use a bimetallic strip that bends when it heats up due to excess current. The bending of the strip causes the breaker to trip, interrupting the current.
Magnetic Circuit Breakers: These use an electromagnet to trip the breaker when the current exceeds a preset limit. The magnetic field generated by the excessive current pulls the contact apart, cutting off the flow of electricity.
Thermomagnetic Circuit Breakers: These combine both thermal and magnetic elements, offering a more comprehensive protection system. They can detect both overloads (using thermal protection) and short circuits (using magnetic protection).
Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCB): These detect leakage currents that may occur due to faults in the electrical system. RCCBs help in preventing electrocution by immediately cutting off power when leakage is detected.
Working Mechanism
Overload Protection: When a circuit is overloaded, the excessive current heats up the bimetallic strip (in thermal breakers) or energizes the electromagnet (in magnetic breakers). This heating or magnetization causes the mechanism to trip, breaking the circuit.
Short Circuit Protection: A short circuit occurs when the current bypasses the normal load, usually due to a fault. In magnetic circuit breakers, the rapid increase in current creates a strong magnetic field, which quickly trips the breaker. Thermal breakers might be slower in detecting this, but once the circuit is overloaded, they will trip after a delay.
Resetting: After the circuit breaker trips, it must be manually reset. Some circuit breakers are designed to reset automatically after the fault is cleared, ensuring continuous protection without manual intervention.
Importance of Circuit Breakers
Protection: The main purpose of a circuit breaker is to safeguard electrical systems and prevent fires, equipment damage, and electrical shock hazards.
Efficiency: By detecting faults in the circuit quickly, circuit breakers help in reducing system downtime and maintaining operational continuity.
Compliance: Circuit breakers are crucial for meeting safety standards and electrical regulations in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Applications
Residential: In homes, circuit breakers protect household appliances and wiring from electrical faults. They are usually located in the main electrical panel.
Industrial: In industrial setups, circuit breakers are used to protect heavy machinery, control panels, and other equipment from overloads and short circuits.
Commercial: Circuit breakers in commercial buildings ensure that electrical systems remain operational and protected from faults.
Conclusion
Circuit breakers play a critical role in ensuring the safety and longevity of electrical systems. They are designed to detect and interrupt dangerous electrical faults, preventing costly damage and hazards. By understanding their types and how they work, we can appreciate their importance in safeguarding our homes, businesses, and industries.




Comment
(0)